Chapter 15 ( Creating Collaborative Partnership )
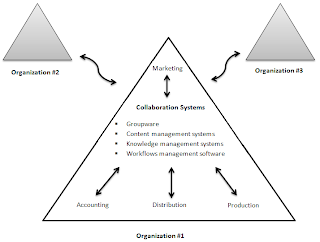
Chapter 15 – Creating Collaborative Partnerships TEAMS, PARTNERSHIPS AND ALLIANCES Ø Organizations create and use teams, partnerships and alliances to; § Undertake new initiatives § Address both minor and major problems § Capitalize on significant opportunities Ø Organizations create teams, partnerships and alliances both internally with employees and externally with other organizations Ø Collaboration system – supports the work of teams by facilitating the sharing and flow of information Information partnerships with other organizations Ø Organizations from alliance and partnerships with other organizations based on their core competency § Core competency – An organization’s key strength, a business function that it does better than any of its competitors § Core competency strategy – Organization chooses to focus specifically on its core competency and forms partnerships with other organizations to handle nonstrategic bus